In this blog post, our Machine analyst divulges energy efficiency in marine transportation. Most organisations spend 22% of their time on internet research to find that one document that moves the needle. However, we’ve used our Insights Automation Platform (IAP) to analyse thousands of unstructured data sources exploring how renewable energy is transforming the marine industry while protecting the planet.
Ships transport over 10 billion metric tons of cargo annually, responsible for 3% of the global greenhouse gas emissions – more emissions than the aviation industry. But the damage is two-fold, as 40% of the cargo weight of these ships consists of fossil fuels or fossil fuel-derived chemicals. An average cargo ship emits 16.14 grams of CO2 per metric ton of cargo shipped per kilometre and as a whole international shipping emitted more than 700 million metric tons of CO2 merely in 2021.
Fuel Efficiency Regulations in the Marine Industry
Such a high level of emissions has raised environmental concerns in the industry. Therefore, adopting energy-efficient measures is on the rise to mitigate these negative impacts while generating economic benefits. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IREA) suggests that if the shipping sector adopts appropriate energy efficiency measures, it could decarbonise by 2050.
Some key regulations that aim to reduce the industry’s impact on the environment and improve the overall efficiency of operations include:
- Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) – a mechanism that allows the shipping industry to use the latest technologies to build vessels
- Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) – a practical approach for ship operators and ship management companies to measure and controls GHG emissions for existing shipping fleets
These Regulations create a framework that compels shipping companies to improve the energy efficiency of their operations, reduce carbon emissions, and minimize environmental impact. The aim is to comply with regulations, achieve long-term sustainability, and reap economic benefits through lower operating costs.
Energy Efficiency in Marine: Key Trends
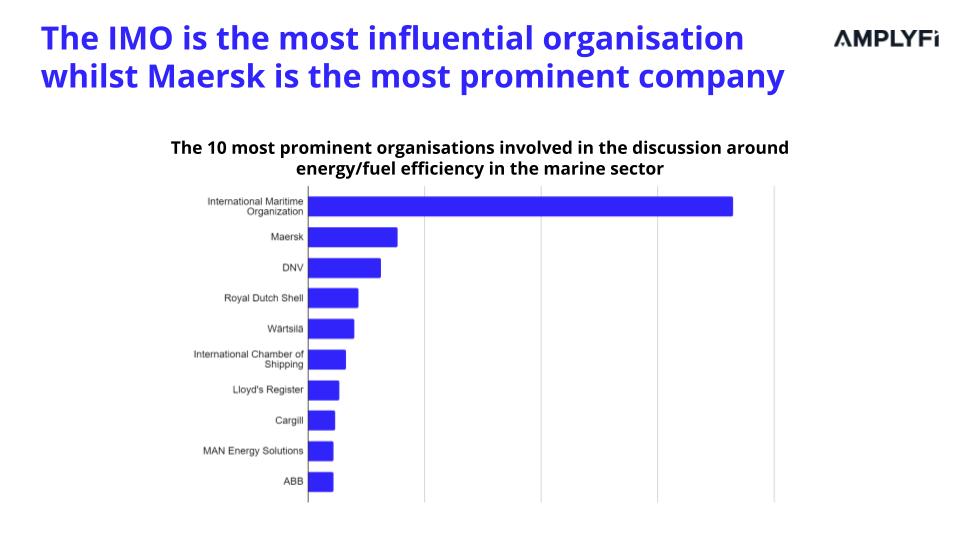
Using AMPLYFI’s AI and Machine Learning technology, we analysed thousands of data sources to determine the most influential organisation and prominent company in the discussion around energy/fuel efficiency in the marine sector. The analysis revealed that the International Maritime Organization (IMO) is the most influential, while Maersk is the most prominent company.
As the world’s largest container company, Maersk contributes to 0.1% of global greenhouse emissions. and therefore prioritised to support the decarbonisation of oceans, terminals and logistics. Maersk has set a target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensity by 50% by 2030. To achieve this, the company aims to increase energy efficiency and adopt low-emission energy sources like alternative fuels and external power. Additionally, our analysis identified the top 10 organisations involved in fuel efficiency discussion.
The Role of Innovation and Collaboration in Achieving Energy Efficiency
Interest in utilising alternative energy sources is growing. Many companies are exploring renewable energy sources like wind and solar power to supplement traditional fuel sources.
Notable innovative organisations in this space include:
| Name | About | Technology |
| MOL | Japanese bulk carrier | Deployed the worlds-first cargo ship with wind assistance, |
| Wallenius | Swedish shipping Company | Intends for its Oceanbird vessel to reduce emissions by up to 90% |
| Zephyr & Borée | French start-up | Constructed the Canopée – the world’s first sail-powered ship – which will transport parts of the European Space Agency’s Ariane 6 rocket in 2024. |
| Maersk | The world’s largest container shipping company | installed hybrid propulsion systems on some of its vessels, with a 10% to 12% reduction in fuel consumption |
| Carnival Corporation | The world’s largest leisure travel company | Implemented waste heat recovery systems on some of its vessels, resulting in a 5% to 10% reduction in fuel consumption. |
In addition, the use of AI-based technologies is on the rise, AI disrupting many industries and the marine sector is no different. Some shipping companies have adopted advanced technologies, such as AI-powered routing systems, to optimise operations, route planning and reduce fuel consumption. For example, Maersk has begun a significant shift towards artificial intelligence by incorporating it into essential ground-level support activities such as handling order reservations and modifications.
However, achieving energy efficiency targets are possible with collaboration and adaptability. Collaborations between port authorities and shipping companies have led to the development of innovative practices, such as cold ironing, where ships are plugged into shore-based electrical power to reduce emissions while in port. Cold ironing was introduced at the West Basin Container Terminal at Berth 100 in the Port of Los Angeles on June 21, 2004, making it the world’s first container terminal to adopt this technology. Similarly, some ports offer shore ironing including the Port of Long Beach, the Port of Seattle and Antwerp, and Greece’s Port of Killini, contributing to energy efficiency targets.
In conclusion, achieving these targets will require significant innovation and collaboration across the industry. Governments, industry associations, and other stakeholders are also investing in research and development to drive innovation in the marine sector. By continuing to invest in and support these efforts, the marine industry can work towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.