Aquaculture, the farming of aquatic organisms including fish, seafood, seaweed and other marine life for human consumption and industrial use, is estimated to be the fastest growing food production sector globally.
Aquaculture immensely contributes to global food security. More than half of the seafood consumed worldwide is sourced from aquatic farms to meet growing demand — the world’s population is expected to require 232 million metric tons of seafood by 2030, 62 million metric tons more than the planet is expected to produce. Alongside the issue of demand, global warming poses a significant threat to aquaculture sustainability due to rising sea levels and ocean temperatures that may undermine the survival of different species, thereby implicating its global food system and value chain.
2022 is the UN International Year of Artisanal Fisheries and Aquaculture (IYAFA 2022), highlighting the importance of aquaculture and artisanal fisheries in contributing to global healthy food systems and economic development. AMPLYFI, using our AI-driven insights tool, have examined themes related to sustainable aquaculture and it’s intersection with climate change, food security and food systems. Our tool delivers unique insights by connecting structured and unstructured data at scale to uncover previously hidden links, trends and opportunities.
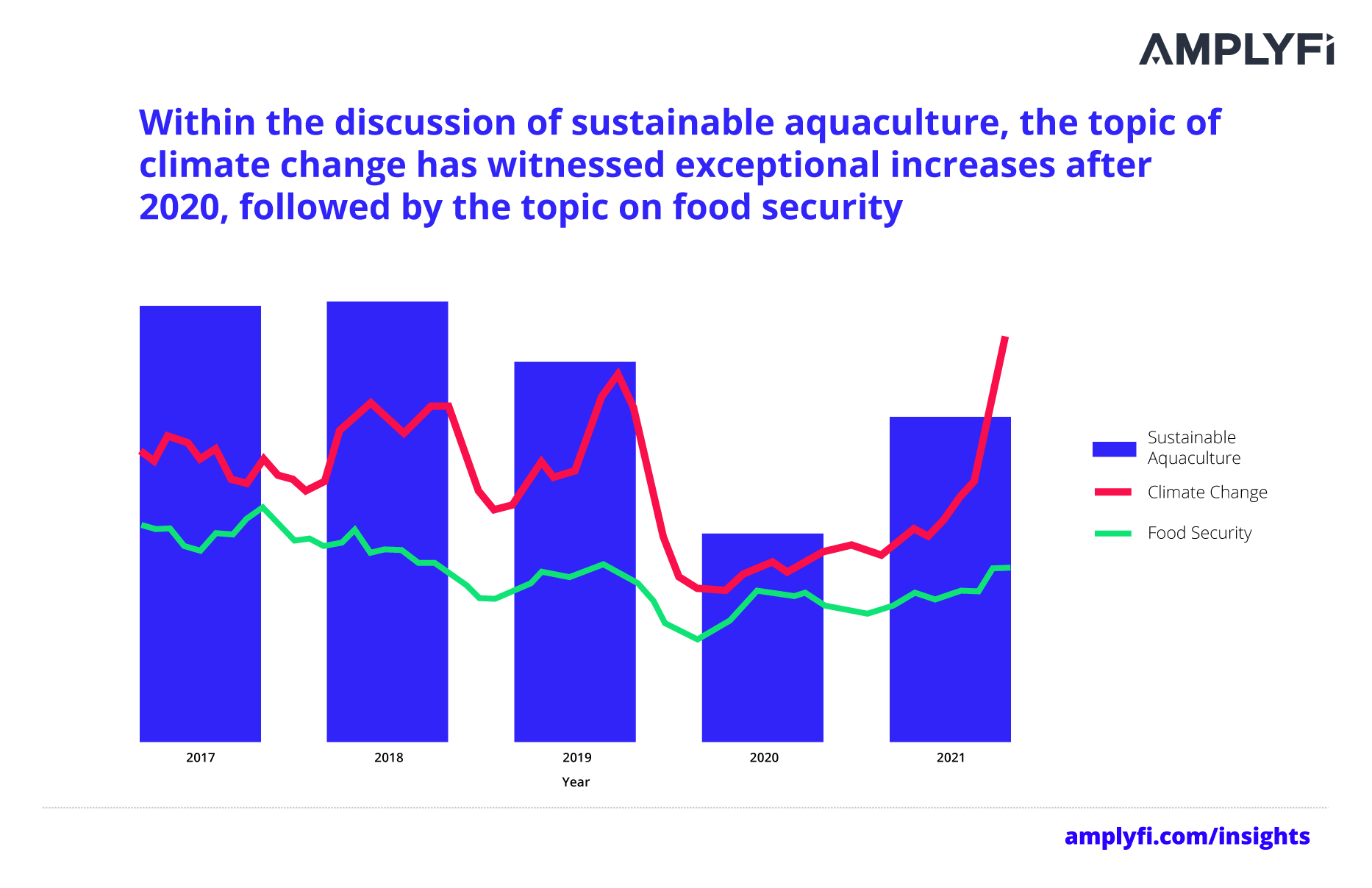
Our analysis shows that, in news document discussions over the past five years, climate change has been highly linked to sustainable aquaculture. With evidence showing that increasing global temperatures could mean 17% less marine life by the end of this century; such a strong connection is expected.
At the onset of the pandemic in 2020, AMPLYFI’s analysis shows a decline in mentions of all three topics, arguably due to the world focusing on understanding COVID-19 implications. From 2021 onwards, climate change gains significance in discussions over sustainable aquaculture and food security. Signifying that, among the consequences of the pandemic, is a heightened awareness of the threat posed by climate change. The 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26), specifically, highlighted aquaculture’s transformative role in food systems, and how it can play a key role in reducing climate change impacts. With climate change undermining marine life, the topic is set to have greater prominence within the context of sustainable aquaculture in the coming years.
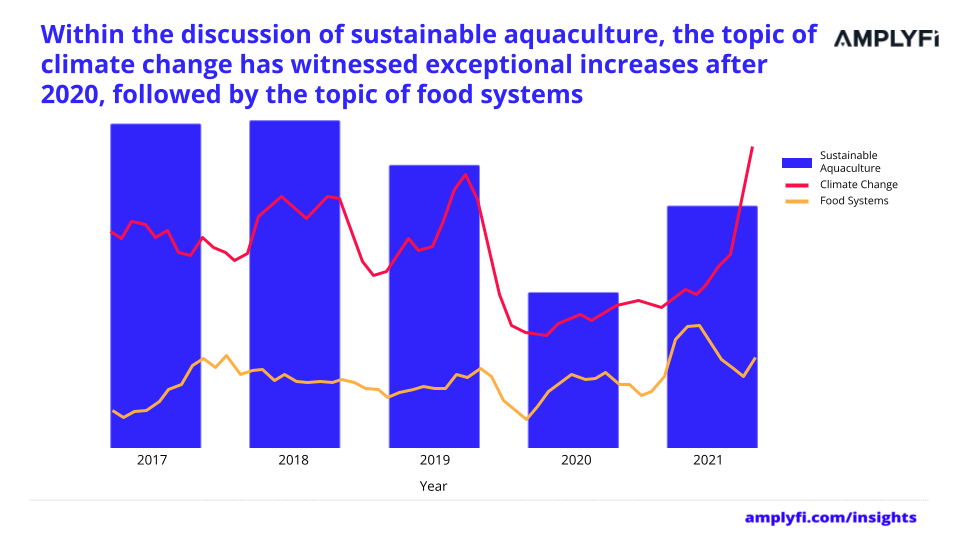
AMPLYFI’s analysis reveals that in the context of food systems and climate change, within the broader aquaculture discussion, the narrative follows a similar trend to that of food security.
The topic of food systems is experiencing a general upward sloping trend in discussions within sustainable aquaculture, suggesting it is rising in prominence. This could be linked to heightened awareness from COP26 of climate patterns, ocean acidity and rising sea levels significantly affecting seafood supply chains. For instance, researchers warn that the productivity of species in deep ocean waters are diminished by increased temperatures.
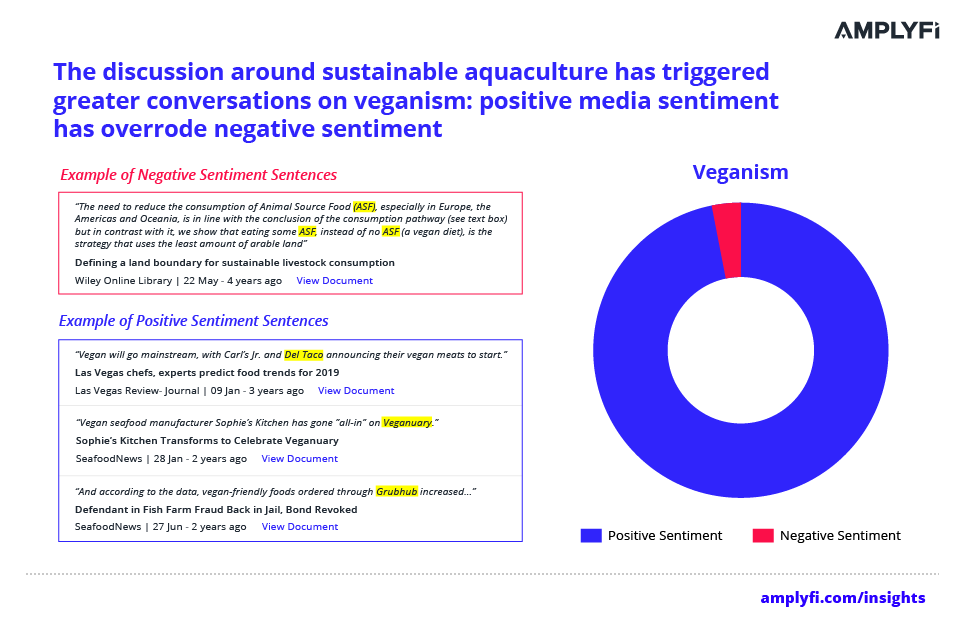
In the midst of climate change mitigation, alternative and plant-based diets are increasing in popularity and have further expanded sustainability in the aquaculture space. Research shows that high levels consumption of meat and dairy produce are contributing to global warming, therefore adopting veganism can help to fight climate change. Efforts to advance veganism within the aquaculture sector include the development of plant-based seafood products for consumers concerned about sustainability, overfishing and ocean pollution.
When analysing media sentiment towards veganism in sustainable aquaculture, AMPLYFI’s DeepInsight platform shows that sentiment towards the topic is primarily positive. Examples of positive sentiment include companies making vegan fish alternatives, and seafood manufacturers getting involved with Veganuary (a Veganism campaign to encourage people to adopt a vegan diet for January).
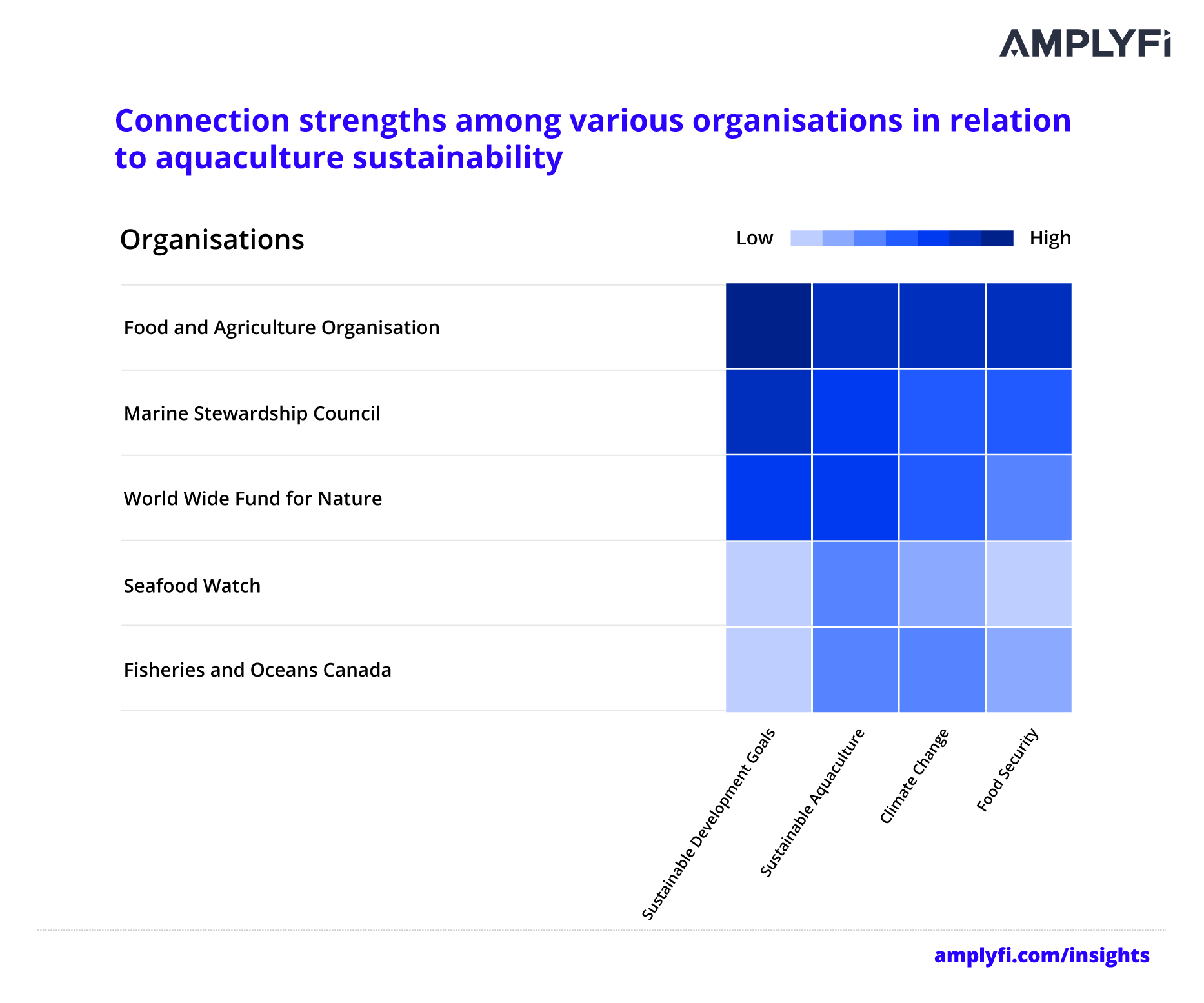
AMPLYFI’s analysis also reveals connection strengths between key organisations and topics from the analysed documents. For example, institutions like the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) have a high connection to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and related topics of sustainable aquaculture, climate change and food security. Aquaculture is a key part of the SDGs, with Goal 2 – Zero Hunger, Goal 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production, Goal 13 – Climate Action and Goal 14 – Life Below Water, all relating to the topic.
Surprisingly, Seafood Watch has a moderate connection to sustainable aquaculture but a weak connection to climate change. Fisheries and Oceans Canada has a moderate link to both sustainable aquaculture and climate change but a weak connection to food security and an even weaker connection to the SDGs.
AMPLYFI’s analysis highlights the strong connection between sustainable aquaculture and maintaining global food systems. This strong connection is alongside the key topic of the threat of climate change, which is set to cause a decline in marine life, undermine food security and cause supply chain disruptions within the sector. Using AMPLYFI’s tool we were able to identify key topic trends, drivers of change and relationships between prominent entities to gain the full picture on sustainable aquaculture today, and where the industry is heading in the future.